VLAN Tags Explained
In the realm of computer networking, the efficient management of network traffic is crucial for ensuring the smooth operation of digital communications. One of the key technologies used to achieve this is the Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN). VLANs allow network administrators to divide a physical network into multiple logical segments, enhancing security, improving performance, and simplifying network management. At the heart of VLAN technology lies the VLAN tag, a critical component that enables the differentiation and routing of traffic across these virtual networks.
Introduction to VLANs
Before diving into the specifics of VLAN tags, it’s essential to understand the basics of VLANs. A VLAN is a logical grouping of devices on a network that are isolated from other devices on the same physical network. This isolation is achieved through the use of VLAN tags, which are added to Ethernet frames to identify the VLAN they belong to. VLANs can be configured based on various criteria, including the need for secure segregation of sensitive data, the optimization of network performance by reducing broadcast traffic, or the logical grouping of devices based on their functions or locations.
What are VLAN Tags?
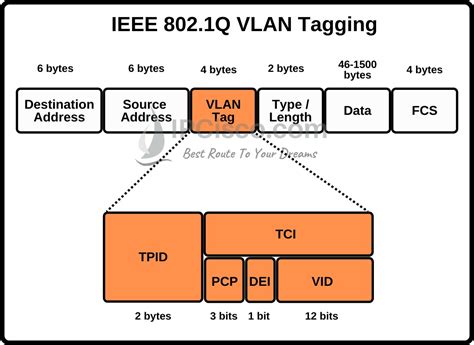
A VLAN tag, also known as an IEEE 802.1Q tag, is a 4-byte (32-bit) field inserted into an Ethernet frame header. This tag contains a 12-bit VLAN ID (VID), which explicitly identifies the VLAN to which the frame belongs. The VLAN ID is used by networking devices to determine how to handle the frame, ensuring that it is delivered only to devices within the same VLAN. The insertion of VLAN tags into Ethernet frames is typically done by network switches and routers that support VLAN functionality.
Components of a VLAN Tag
The VLAN tag includes several components: - TPID (Tag Protocol Identifier): A 16-bit field that identifies the protocol being used. For Ethernet frames, this is set to 0x8100 to indicate an 802.1Q tag. - TCI (Tag Control Information): A 16-bit field containing the VLAN ID and priority information. The VLAN ID is a 12-bit value (allowing for 4096 possible VLANs), and there are 3 bits for class of service (CoS) or priority, which can be used for quality of service (QoS) purposes. - VLAN ID (VID): The 12-bit identifier that specifies the VLAN. VLAN IDs range from 1 to 4094; IDs 0 and 4095 are reserved.
How VLAN Tags Work
The process of using VLAN tags to manage network traffic involves several steps: 1. Assignment: Network devices are assigned to specific VLANs based on their port connections or other criteria. 2. Tagging: When a device sends data, the network switch inserts a VLAN tag into the Ethernet frame if the VLAN feature is enabled. 3. Forwarding: Switches and routers use the VLAN ID in the tag to determine where to forward the frame, ensuring that it only reaches devices within the same VLAN. 4. Removing Tags: When frames are sent from a VLAN to a non-VLAN aware device (like a PC), the switch removes the VLAN tag to prevent confusion, as non-VLAN devices do not understand VLAN tags.
Advantages of VLAN Tags
The use of VLAN tags and VLANs offers several benefits: - Improved Security: By segregating network traffic into separate VLANs, sensitive data can be protected from unauthorized access. - Enhanced Performance: Reducing broadcast traffic within VLANs can improve network performance, as devices only receive traffic intended for them. - Simplified Network Management: Network administrators can manage and troubleshoot networks more easily by dealing with logical rather than physical network segments.
Challenges and Considerations
While VLAN tags are powerful tools for network management, there are challenges and considerations: - Scalability: Managing a large number of VLANs can become complex. - Inter-VLAN Routing: Devices in different VLANs cannot communicate directly and require a router or layer 3 switch to communicate between VLANs. - VLAN Trunking: To extend VLANs across multiple switches, VLAN trunks (links that carry traffic for multiple VLANs) are necessary, requiring careful configuration.
Conclusion
VLAN tags play a crucial role in managing and securing network communications by enabling the creation of virtual local area networks. Understanding how VLAN tags work, their components, and their role in network management is essential for network administrators. By leveraging VLAN technology, organizations can create more secure, efficient, and scalable networks, meeting the demands of an ever-evolving digital landscape.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the purpose of VLAN tags in networking?
+VLAN tags are used to identify which VLAN a frame belongs to, enabling network devices to manage and isolate network traffic efficiently.
How many VLANs can be created using the 802.1Q standard?
+The 802.1Q standard allows for up to 4096 VLANs (VLAN IDs 1-4094), with IDs 0 and 4095 reserved.
What is the difference between a VLAN and a subnet?
+A VLAN is a logical grouping of devices at the data link layer (Layer 2), while a subnet is a logical grouping of IP addresses at the network layer (Layer 3). VLANs and subnets serve different purposes but can be related in network design.