Sensitive Data Classification Guide
In today’s digital age, the handling and protection of sensitive data have become a top priority for organizations across various industries. The mismanagement of sensitive information can lead to severe consequences, including financial losses, reputational damage, and legal repercussions. Therefore, it is crucial to understand the importance of sensitive data classification and implement a robust framework for its management.
Introduction to Sensitive Data
Sensitive data refers to any information that, if compromised, could cause harm to an individual, organization, or entity. This includes but is not limited to personal identifiable information (PII), financial data, health records, intellectual property, and confidential business information. The sensitivity of data can vary depending on the context and the potential impact of its disclosure.
Why Classify Sensitive Data?
Classifying sensitive data is essential for several reasons:
- Risk Management: By categorizing data based on its sensitivity, organizations can better manage risks associated with data breaches and unauthorized access.
- Compliance: Many regulatory frameworks, such as GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS, require the classification and protection of sensitive data.
- Data Protection: Classification helps in implementing appropriate security controls to protect sensitive data from unauthorized access, theft, or damage.
- Efficient Data Handling: Classification facilitates the efficient handling of data by ensuring that sensitive information is only accessible to authorized personnel.
Sensitive Data Classification Framework
A robust sensitive data classification framework typically consists of the following categories:
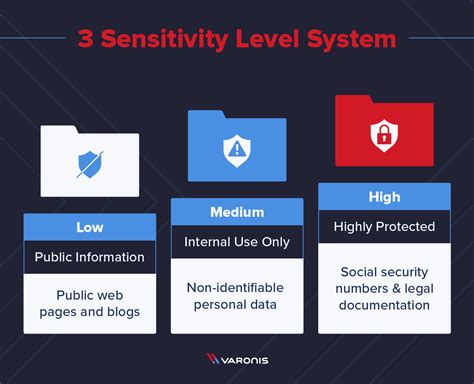
- Public Data: Information that is freely available and can be accessed by anyone without restrictions.
- Internal Data: Information that is intended for internal use within an organization and is not sensitive in nature.
- Confidential Data: Sensitive information that, if disclosed, could cause harm to an individual or the organization. This includes PII, financial data, and confidential business information.
- Restricted Data: Highly sensitive information that requires strict access controls and is typically only accessible to authorized personnel. This includes intellectual property, trade secrets, and critical infrastructure information.
- Top Secret Data: Extremely sensitive information that, if compromised, could cause catastrophic harm to an individual, organization, or national security.
Classification Criteria
When classifying sensitive data, consider the following criteria:
- Impact of Disclosure: The potential harm caused by the disclosure of the information.
- Value to the Organization: The importance of the information to the organization’s operations, reputation, or financial well-being.
- Regulatory Requirements: Compliance with relevant laws, regulations, and industry standards.
- Data Sensitivity: The level of sensitivity associated with the information, such as personal or financial data.
Best Practices for Sensitive Data Classification
- Develop a Clear Classification Policy: Establish a well-defined classification framework and communicate it to all employees.
- Train Employees: Provide regular training on sensitive data classification and handling procedures.
- Use Access Controls: Implement strict access controls, including encryption, authentication, and authorization.
- Monitor and Audit: Regularly monitor and audit data access and handling practices to ensure compliance with the classification framework.
- Review and Update: Periodically review and update the classification framework to ensure it remains relevant and effective.
Tools and Technologies for Sensitive Data Classification
Several tools and technologies can aid in sensitive data classification, including:
- Data Loss Prevention (DLP) Tools: Software solutions that detect and prevent sensitive data from being leaked or misused.
- Encryption Technologies: Methods for protecting sensitive data both in transit and at rest.
- Access Control Systems: Solutions that regulate access to sensitive data based on user identity, role, and permissions.
- Classification Software: Tools that automate the classification process, such as data discovery and classification platforms.
Challenges and Limitations
While sensitive data classification is crucial, it also presents several challenges and limitations, including:
- Data Volume and Complexity: The sheer volume and complexity of data can make classification a daunting task.
- Human Error: Employees may misclassify or mishandle sensitive data due to lack of training or awareness.
- Evolving Regulatory Landscape: Keeping up with changing regulatory requirements and standards can be challenging.
- Balancing Security and Productivity: Implementing strict security controls can sometimes hinder productivity and efficiency.
Conclusion
Sensitive data classification is a critical component of any organization’s data protection strategy. By understanding the importance of classification, developing a robust framework, and implementing best practices, organizations can effectively manage and protect sensitive information. While challenges and limitations exist, the benefits of sensitive data classification far outweigh the costs, and it is essential for maintaining the trust and confidence of customers, employees, and stakeholders.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is sensitive data classification?
+Sensitive data classification is the process of categorizing data based on its sensitivity and potential impact of disclosure. It helps organizations manage risks, ensure compliance, and protect sensitive information.
Why is sensitive data classification important?
+Sensitive data classification is crucial for managing risks, ensuring compliance with regulatory requirements, and protecting sensitive information from unauthorized access or disclosure.
What are the common categories of sensitive data classification?
+Common categories include Public Data, Internal Data, Confidential Data, Restricted Data, and Top Secret Data. Each category has distinct characteristics and requires specific handling and protection procedures.
How can organizations implement effective sensitive data classification?
+Organizations can implement effective sensitive data classification by developing a clear classification policy, training employees, using access controls, monitoring and auditing, and regularly reviewing and updating the classification framework.
What tools and technologies can aid in sensitive data classification?
+Tools and technologies such as Data Loss Prevention (DLP) tools, encryption technologies, access control systems, and classification software can aid in sensitive data classification and protection.



