DNS Attacked
The ever-present threat of cyberattacks has once again reared its head, this time in the form of a DNS attack. For those who may be unfamiliar, a DNS (Domain Name System) attack occurs when an individual or group attempts to exploit vulnerabilities in the DNS, which is essentially the phonebook of the internet, translating domain names into IP addresses that computers can understand. This critical infrastructure is what allows us to access websites, send emails, and conduct other online activities with ease.
Understanding the Impact of a DNS Attack
A DNS attack can have far-reaching consequences, affecting not only the targeted organization but also its customers, partners, and the broader internet community. Some of the most common types of DNS attacks include:
- DNS Spoofing: This involves manipulating DNS responses, redirecting users to fake or malicious websites. This can lead to phishing, malware distribution, and other types of cyber threats.
- DNS Amplification: A type of distributed denial-of-service (DDoS) attack where an attacker exploits the fact that DNS response packets are typically larger than DNS query packets. By spoofing the source IP address of the DNS query, the attacker can flood the targeted system with large DNS responses.
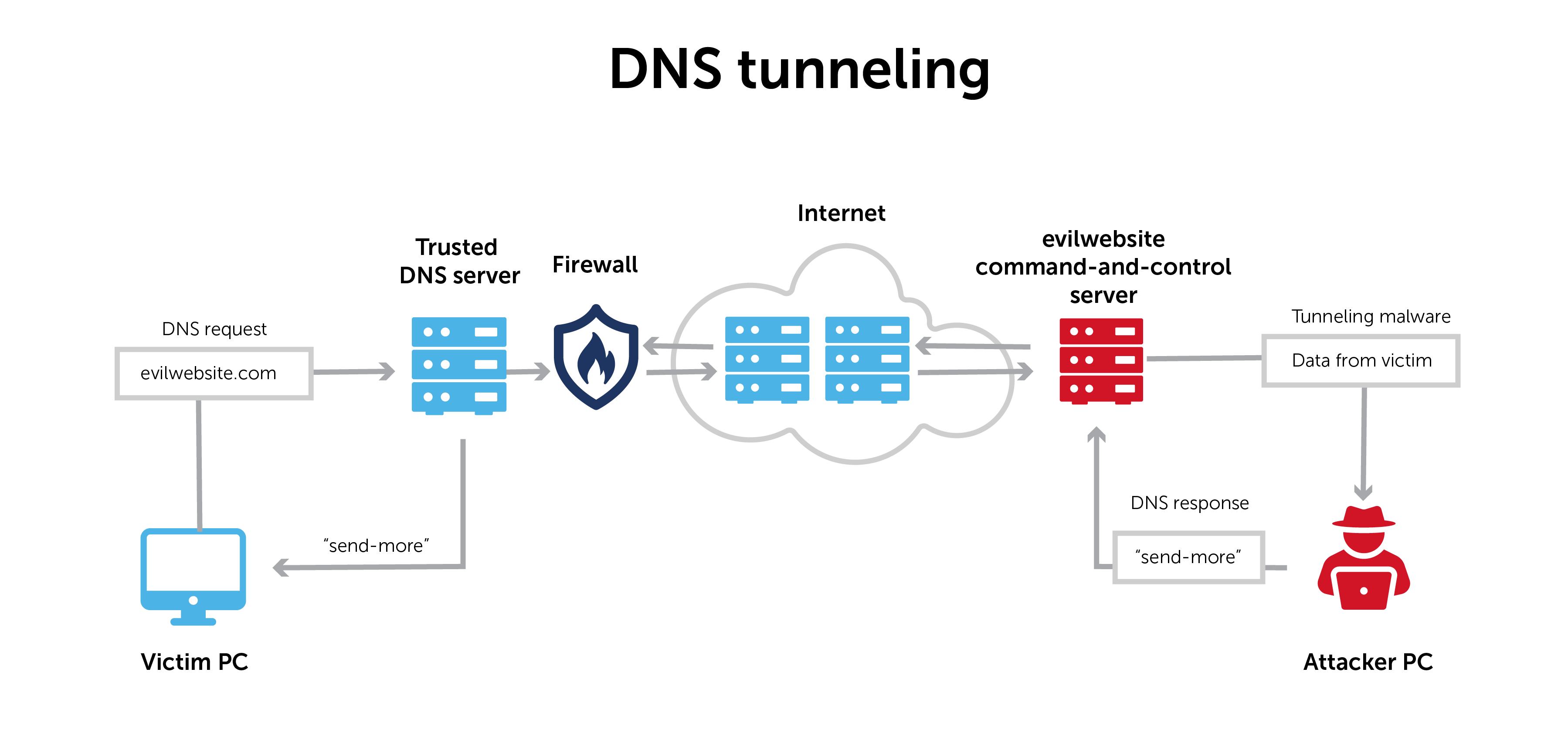
- DNS Tunneling: This technique involves using the DNS protocol to tunnel malware or other data through a network, bypassing security controls and allowing attackers to establish command and control channels.
Mitigating DNS Attacks
Given the potential impact of a DNS attack, it’s crucial for organizations to implement robust mitigation strategies. Some key measures include:
Implementing DNSSEC: DNS Security Extensions (DNSSEC) is a suite of extensions that add an additional layer of security to the DNS protocol by providing authentication and integrity. This can prevent DNS spoofing and ensure that DNS responses are genuine.
Using a Reputable DNS Service: Selecting a DNS service provider that has a strong focus on security can significantly reduce the risk of DNS attacks. Such providers often implement advanced security measures, including DNS firewalls and traffic analysis tools.
Regularly Updating and Patching Systems: Keeping all systems, especially those involved in DNS resolution, updated with the latest security patches can prevent exploitation of known vulnerabilities.
Educating Users: Conducting regular cybersecurity awareness training can help prevent users from falling victim to phishing attempts and other social engineering tactics that might be used in conjunction with DNS attacks.
The Role of Artificial Intelligence in DNS Security
The integration of Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) into DNS security is offering new avenues for threat detection and mitigation. AI can analyze vast amounts of DNS traffic data to identify patterns that may indicate a DNS attack. This includes detecting anomalies in query patterns, which can signal a potential attack before it causes significant harm. Furthermore, AI-driven systems can automatically update DNS security policies and block malicious traffic in real-time, significantly enhancing response times to emerging threats.
Future Trends in DNS Security
As DNS attacks continue to evolve in complexity and sophistication, so too must the defensive strategies. Future trends in DNS security are likely to include:
Increased Adoption of Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: With the advent of quantum computing, there is a growing need for cryptographic algorithms that are resistant to quantum attacks. Implementing quantum-resistant cryptography in DNSSEC will be crucial for long-term security.
Greater Emphasis on DNS Over HTTPS (DoH): DoH encrypts DNS queries, making it more difficult for attackers to intercept and manipulate DNS traffic. As privacy and security concerns continue to grow, the adoption of DoH is expected to increase.
Advanced Threat Intelligence: Leveraging threat intelligence can help organizations stay ahead of emerging DNS threats. This involves not just analyzing DNS traffic but also integrating information from various sources to predict and prepare for potential attacks.
In conclusion, while DNS attacks pose a significant threat to online security, a combination of traditional security measures, advanced technologies like AI, and proactive strategies can effectively mitigate these risks. As the cyber landscape continues to evolve, it’s essential for organizations and individuals alike to remain vigilant and adapt their security practices to protect against the ever-present threat of DNS attacks.
What is the primary purpose of DNSSEC?
+DNSSEC, or Domain Name System Security Extensions, is primarily used to add an additional layer of security to the DNS protocol by providing authentication and integrity, thus preventing DNS spoofing attacks.
How does DNS amplification work?
+DNS amplification is a type of DDoS attack that exploits the difference in size between DNS queries and responses. An attacker sends a DNS query with a spoofed source IP address to a DNS server, which then responds with a much larger DNS response packet to the spoofed IP address, leading to a flood of traffic.
What role does AI play in enhancing DNS security?
+AI and ML technologies are used to analyze DNS traffic patterns to detect anomalies and potential threats in real-time, enabling quicker and more effective responses to DNS attacks. They can also help in predicting and mitigating future threats by analyzing historical data and trends.



