Define QoS Network Quality
Quality of Service (QoS) network quality refers to the ability of a network to provide a guaranteed level of service performance for specific applications, users, or data flows. It encompasses various aspects of network behavior, including throughput, latency, jitter, packet loss, and availability, to ensure that critical applications and services receive the necessary network resources to function optimally.
QoS is crucial in modern networks, where diverse applications with varying requirements coexist. For instance, real-time applications like video conferencing, online gaming, and VoIP (Voice over Internet Protocol) require low latency and jitter to ensure smooth communication. In contrast, non-real-time applications like file transfers and email may tolerate higher latency but still require reliable delivery.
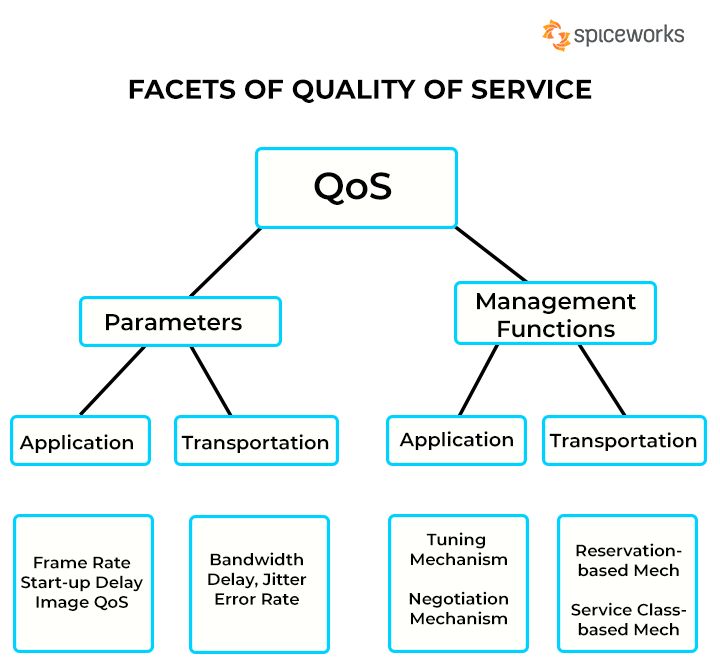
Key parameters that define QoS network quality include:
- Throughput: The amount of data that can be transmitted over a network within a given time frame, usually measured in bits per second (bps).
- Latency: The time it takes for data to travel from the source to the destination, also known as delay or ping time.
- Jitter: The variation in latency, which can cause packets to arrive out of order or with varying delays.
- Packet Loss: The percentage of packets that fail to reach their destination, often due to network congestion or errors.
- Availability: The percentage of time the network is operational and accessible to users.
To ensure high QoS network quality, network administrators and service providers employ various techniques, including:
- Traffic Classification: Identifying and categorizing traffic based on its type, priority, and requirements.
- Traffic Shaping: Regulating the amount of traffic that can be sent or received by a particular application or user.
- Traffic Policing: Dropping or marking packets that exceed predetermined rate limits.
- Queue Management: Managing the order and priority of packets in network buffers to minimize latency and packet loss.
- Resource Reservation: Allocating dedicated network resources, such as bandwidth and buffer space, to critical applications.
- Network Monitoring: Continuously monitoring network performance and adjusting QoS policies as needed.
QoS network quality is essential for various industries and applications, including:
- Real-time Communications: VoIP, video conferencing, and online gaming.
- Cloud Computing: Ensuring reliable and low-latency access to cloud-based services.
- Financial Services: Supporting high-speed and secure transactions.
- Healthcare: Enabling timely and reliable access to medical records and telemedicine services.
- Education: Providing high-quality online learning experiences.
In summary, QoS network quality is a critical aspect of modern networking, as it ensures that networks can provide the necessary performance, reliability, and security for diverse applications and services. By understanding and managing QoS parameters, network administrators can guarantee a high level of service quality, supporting the needs of various industries and applications.
QoS Network Quality Metrics
The following metrics are commonly used to evaluate QoS network quality:
- Mean Opinion Score (MOS): A subjective measure of voice or video quality, ranging from 1 (bad) to 5 (excellent).
- Round-Trip Time (RTT): The time it takes for a packet to travel from the source to the destination and back.
- Packet Loss Rate: The percentage of packets that fail to reach their destination.
- Jitter: The variation in latency, measured in milliseconds.
- Throughput: The average rate of successful data transfer, measured in bits per second (bps).
- Network Availability: The percentage of time the network is operational and accessible to users.
QoS Network Quality Standards
Several standards and frameworks have been developed to ensure QoS network quality, including:
- ITU-T G.1010: A recommendation for network performance parameters and objectives.
- RFC 2544: A benchmarking methodology for network performance.
- IEEE 802.1Q: A standard for virtual local area networks (VLANs) and QoS.
- DiffServ (Differentiated Services): A framework for classifying and managing network traffic.
By understanding and implementing these standards, network administrators can ensure high QoS network quality, supporting the needs of diverse applications and services.
When designing and implementing QoS policies, it's essential to consider the specific requirements of each application and user group. A well-planned QoS strategy can significantly improve network performance, reliability, and security, ultimately leading to increased user satisfaction and productivity.
QoS Network Quality Challenges
Despite the importance of QoS network quality, several challenges can arise, including:
- Network Complexity: The increasing complexity of modern networks, with multiple devices, protocols, and applications, can make it difficult to manage QoS.
- Traffic Growth: The rapid growth of network traffic, driven by emerging technologies like IoT and 5G, can overwhelm network resources and compromise QoS.
- Security Threats: Cybersecurity threats, such as DDoS attacks and malware, can compromise network availability and QoS.
- Limited Resources: Insufficient network resources, such as bandwidth and buffer space, can limit the ability to guarantee QoS.
To address these challenges, network administrators must employ advanced QoS management techniques, such as machine learning and artificial intelligence, to optimize network performance and ensure high QoS network quality.
QoS Network Quality Best Practices
The following best practices can help ensure high QoS network quality:
- Monitor Network Performance: Continuously monitor network performance, using tools like packet capture and analysis software.
- Implement QoS Policies: Develop and implement QoS policies that prioritize critical applications and traffic.
- Optimize Network Configuration: Optimize network configuration, including buffer sizes, queue management, and traffic shaping.
- Ensure Network Security: Ensure network security, using firewalls, intrusion detection systems, and encryption.
- Test and Validate: Test and validate QoS policies, using benchmarking tools and simulation software.
By following these best practices, network administrators can ensure high QoS network quality, supporting the needs of diverse applications and services.
What is the primary goal of QoS network quality?
+The primary goal of QoS network quality is to ensure that networks provide a guaranteed level of service performance for specific applications, users, or data flows.
What are the key parameters that define QoS network quality?
+The key parameters that define QoS network quality include throughput, latency, jitter, packet loss, and availability.
What techniques are used to ensure high QoS network quality?
+Techniques used to ensure high QoS network quality include traffic classification, traffic shaping, traffic policing, queue management, resource reservation, and network monitoring.